Female-biased introductions produce higher predicted population size and genetic diversity in simulations of a small, isolated tiger (Panthera tigris) population
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
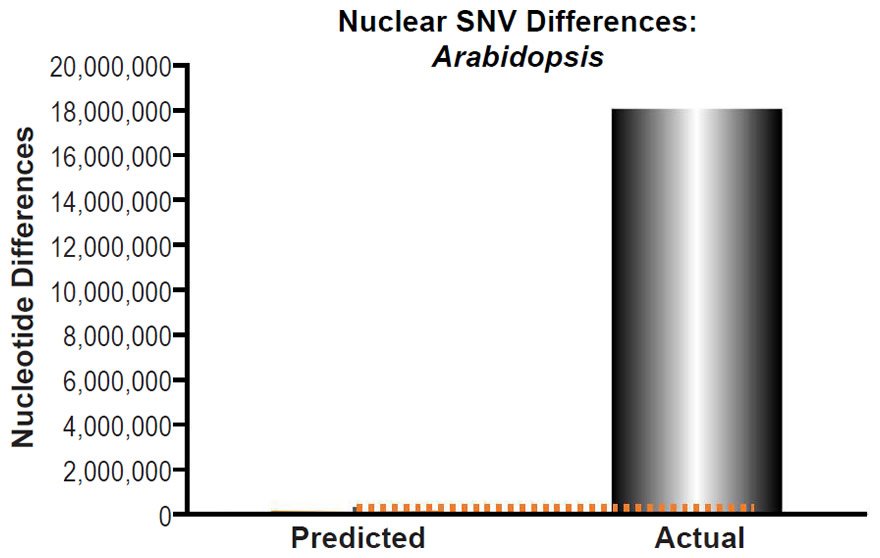
Origin Eukaryotic Genotypic Phenotypic Diversity

ABC 45-2 (2022) by Museu Ciències Naturals de Barcelona MCNB - Issuu

PDF) Comparative genetic analysis of reproductive parameters

Genome-wide signatures of complex introgression and adaptive
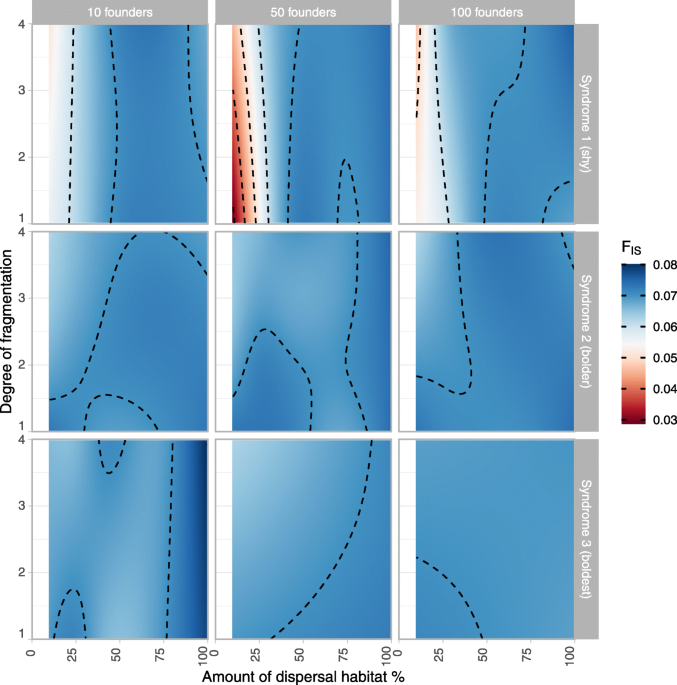
The boon and bane of boldness: movement syndrome as saviour
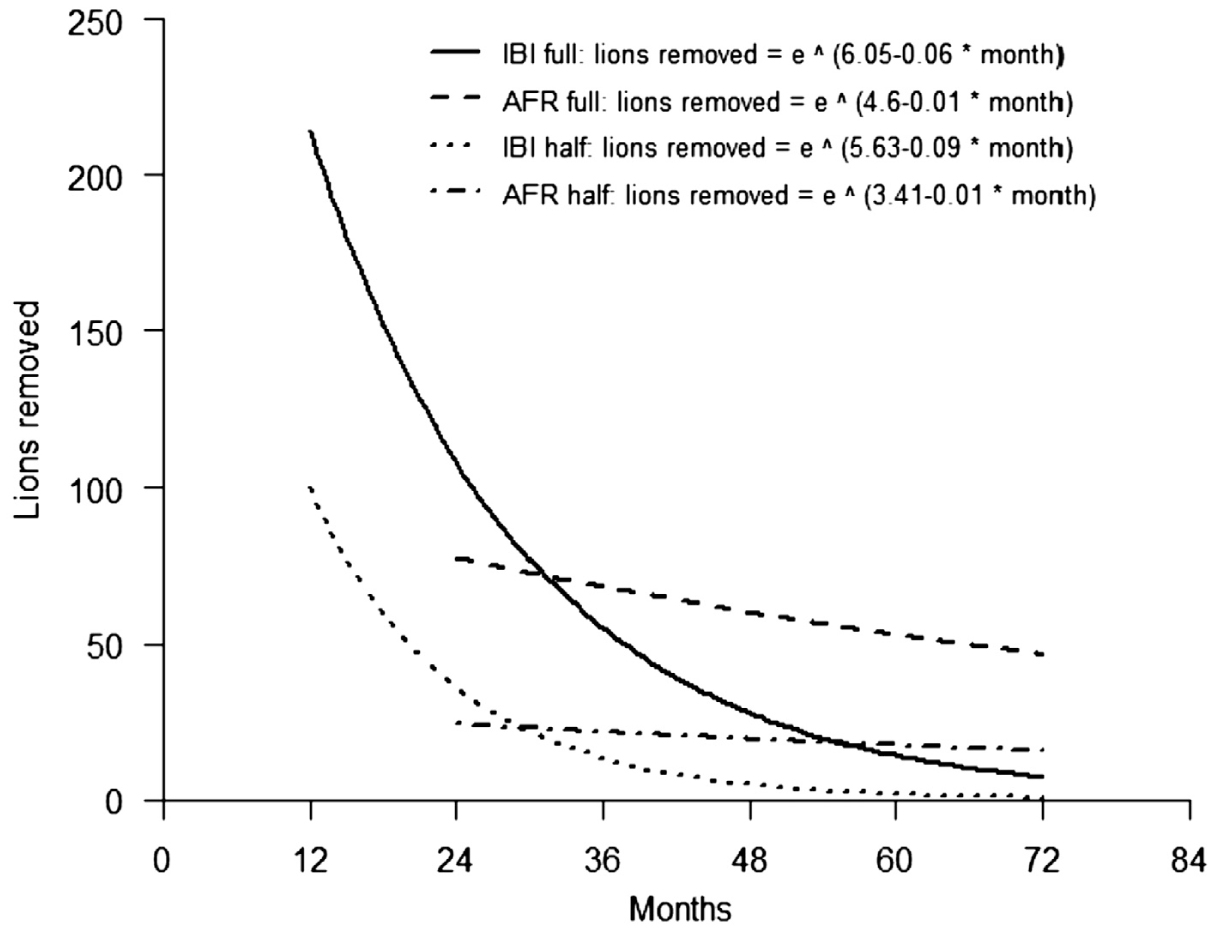
GrowLS: Lion (Panthera leo) Population Growth Simulation for Small
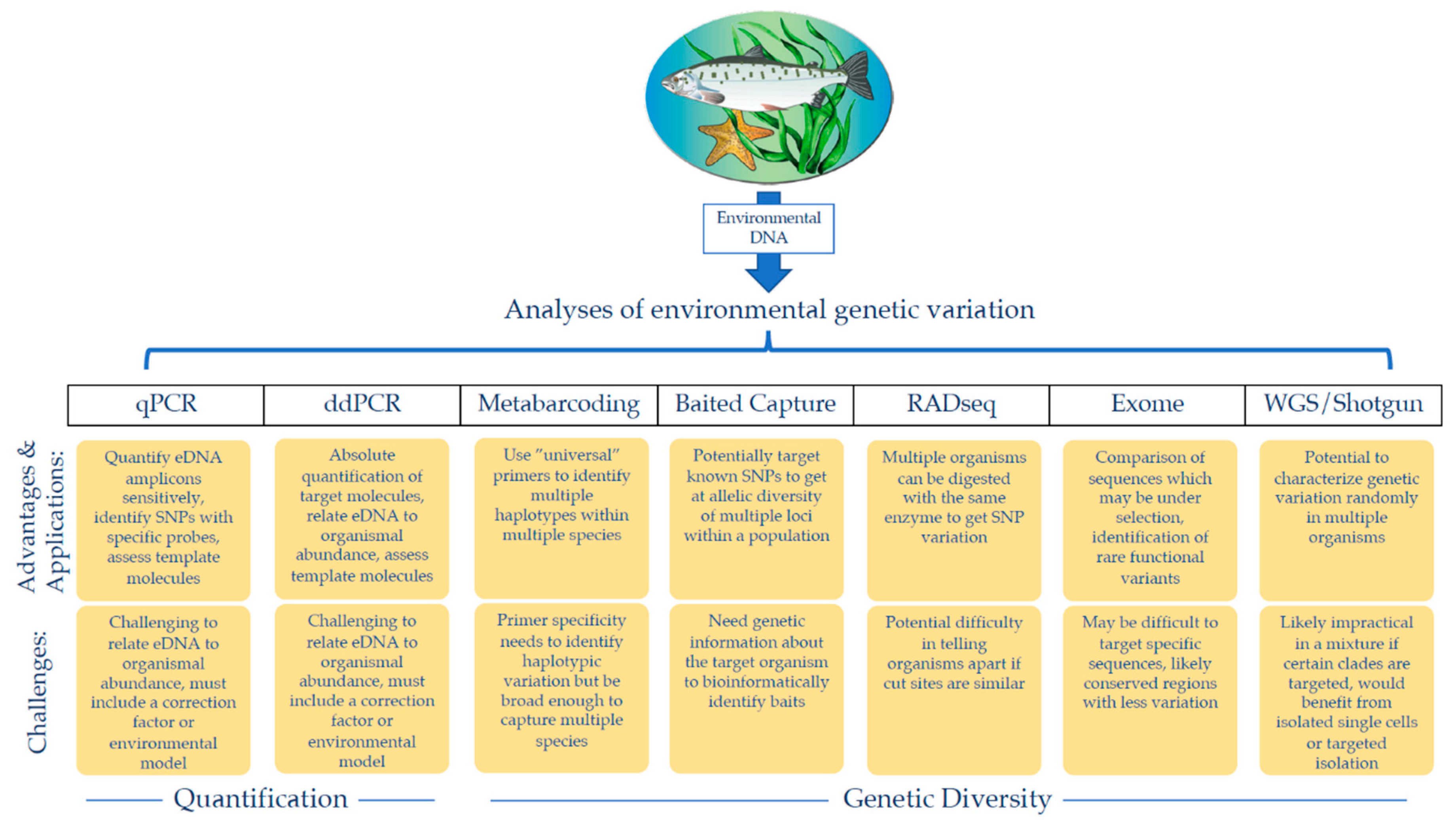
Genes, Free Full-Text
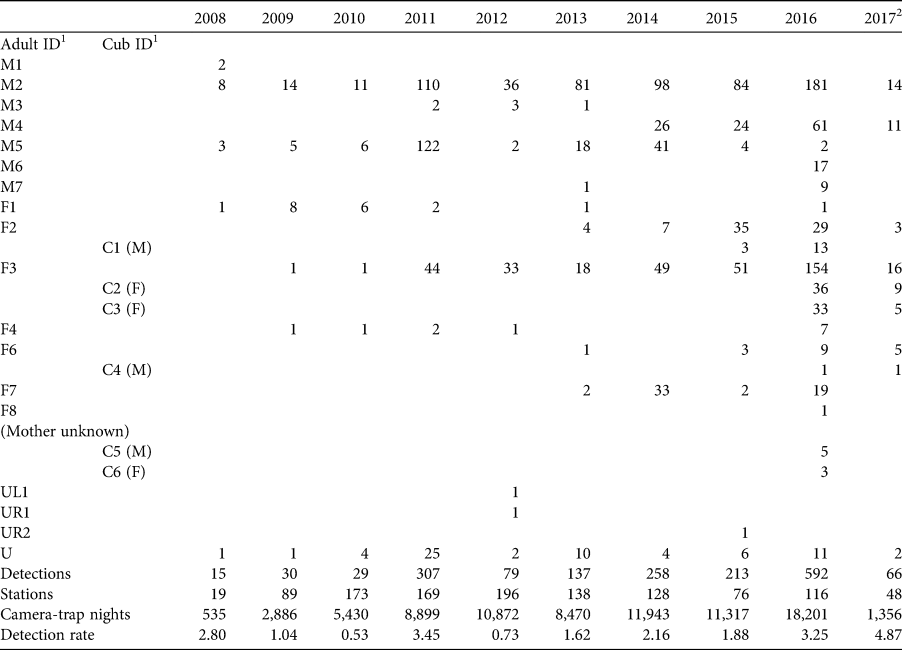
Opportunity for Thailand's forgotten tigers: assessment of the

Demographic Stochasticity and Social Mating System in the Process

Fine-scale population structure and sex-biased dispersal in
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)