Replicatively senescent cells are arrested in G1 and G2 phases - Figure F1
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Senescent human fibroblast cultures contain a large fraction of putative G2-arrested cells with 4N DNA content. (A) Propidium iodide (PI) staining and flow cyctometric analysis of HCA2 normal human foreskin fibroblasts. Cells entered senescence at PD73. (B) PI staining of replicatively senescent human lung fibroblasts WI-38, and IMR-90 at PDs 73 and 68 respectively. (C) The fraction of 4N cells in senescent cell population does not diminish with time. Replicatively senescent HCA2 cells were analyzed by PI staining at weekly intervals for 10 weeks stating from the onset of senescence.

Cell cycle analysis of senescent astrocytes. (A) Representative

Necessary and Sufficient Role for a Mitosis Skip in Senescence

Cellular senescence preserves viral genome maintenance

Exploiting replicative stress in gynecological cancers as a

Cellular Senescence: From Mechanisms to Current Biomarkers and

Cell Cycle and Factors Involved in Inhibition or Progression of
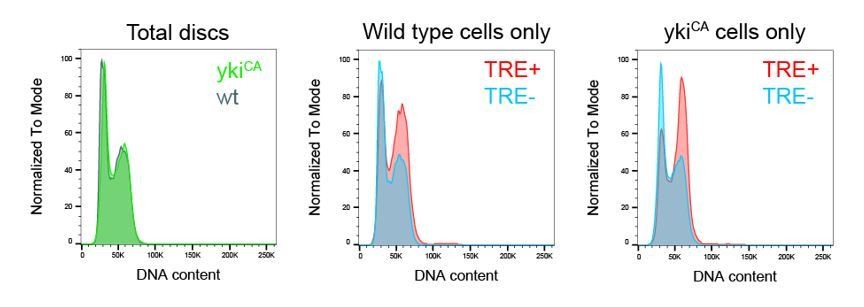
JNK-dependent cell cycle stalling in G2 promotes survival and

The molecular architecture of cell cycle arrest

G1 and G2: What Happens in the Growth Phases of The Cell Cycle?

G2/M cell cycle arrest and senescence-like changes induced by PPKO

Reciprocal regulation of p21 and Chk1 controls the Cyclin D1-RB
Single-cell transcriptomic analysis uncovers diverse and dynamic
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)